What Are Large Language Models? The Ultimate Guide to AI Language Technology in 2025
If you’ve chatted with a virtual assistant, received eerily spot-on recommendations, or marveled at the human-like text coming from AI tools lately, you’ve already crossed paths with large language models—whether you realize it or not. They’re behind the scenes, helping shape everything from business emails to bedtime stories to software code. But what exactly are these language models everyone’s talking about?
Why have they exploded onto the tech scene, and what can they really do for us? This deep dive unpacks the essentials of large language models (LLMs), demystifies their technology, and explores their growing place in our daily lives.

Introduction to Large Language Models
Definition of Large Language Models
Large language models, or LLMs, are a specialized breed of artificial intelligence built to understand and generate text that sounds astonishingly human. When we say “large,” we’re not exaggerating—these models are trained on enormous piles of text data, sometimes containing hundreds of billions of words and parameters (think: the dials and knobs inside the AI’s brain that help it make decisions).
These intricate networks can read, write, summarize, translate, and even reason with language—all by learning the patterns and logic humans use every day.
What’s so magical about these systems is that they don’t operate by following hardcoded rules. Instead, LLMs soak up knowledge from examples, and the result is a tool that can do everything from writing code to penning poetry. They’re the engines inside today’s AI chatbots, creative writers, and digital problem-solvers.
Brief History and Evolution
The evolution of language AI started humbly, with basic rule-based systems—the kind that might recognize a list of keywords but stumble if you strayed off-script. Once machine learning arrived, models like n-grams tried to predict the next word by counting how often phrases appear. But their memory stretched only a few words back, making them limited storytellers.
The real game-changer came with neural networks, then deep learning, and above all, the “transformer” architecture introduced in 2017. Suddenly, LLMs could scan huge amounts of text all at once and pick up subtle context cues—remembering not just a few words, but whole paragraphs at a time.
Since then, AI language technology has raced ahead. GPT, BERT, and a growing list of others now generate text with a fluency that can be hard to distinguish from the real thing.

How Do Large Language Models Work?
Key Technologies Behind LLMs (Neural Networks, Deep Learning, Transformers)
Peek under the hood of a large language model and you’ll find what’s known as a neural network—a vast web of “neurons” and connections designed to mimic, in part, how a human brain processes information. Early neural networks were clever enough, but deep learning took things to the next level by stacking layer upon layer, allowing the model to learn more complex patterns.
But here’s the real secret sauce: the transformer architecture. Instead of reading text word by word, transformers use something called attention, which lets the model focus on the most important words or phrases—whether they’re right next to each other or chapters apart. That’s how LLMs generate context-aware, surprisingly coherent responses, and why they operate so rapidly.
Training Process of LLMs
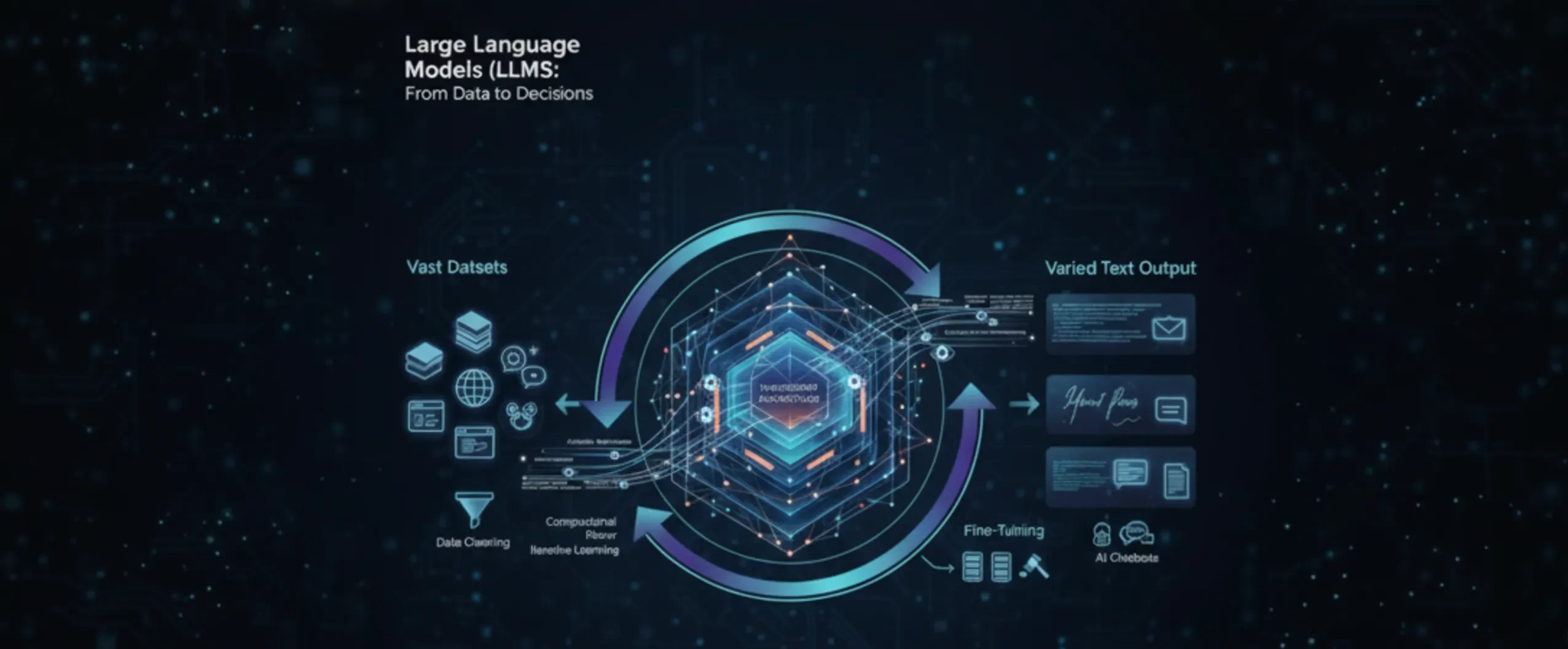
Every LLM starts with a marathon training process:
- Vast datasets—think Wikipedia, classic novels, social media posts, and more—are gathered from across the internet.
- This raw text is cleaned and prepped, then fed into the neural net, which tests itself by guessing the next word over and over.
- With time, and lots of computational power (sometimes thousands of GPUs humming for weeks), the model gets frighteningly good at predicting what comes next.
- After this pre-training, models can be fine-tuned for specific skills—medical writing, legal documents, customer service, you name it. The result? A digital chameleon that adapts its voice and expertise to whatever’s needed.
Popular Examples of Large Language Models
GPT Series (OpenAI)
OpenAI GPT models have set the gold standard for LLMs. It started with GPT-2, which could spin stories that made readers do a double take, then leaped to GPT-3—which boasts 175 billion parameters, making it mind-blowingly versatile. GPT-4 took things even further, bringing stronger reasoning, longer memory, and even the power to explain its own decisions.
These models aren’t one-trick ponies. They’re the foundation of tools like ChatGPT, driving conversation, supporting customer queries, drafting emails, and more. Businesses worldwide
Yes AI
Tel. : 096-879-5445
LINE : @yeswebdesign
E-mail : info@yeswebdesignstudio.com
Address : 17th Floor, Wittayakit Building, Phayathai Rd, Wang Mai, Pathum Wan, Bangkok 10330
(BTS SIAM STATION)
